Have you ever wondered how AI chatbots have evolved from basic rule-based systems to complex AI-driven tools?
This guide takes you through the evolution of AI chatbots, from early models like Eliza and ALICE to today’s advanced systems reshaping industries such as e-commerce, banking, and logistics. Discover how Transformer Neural Networks and language models like ChatGPT and Bard transform digital interactions and fuel market growth.
Today, the global AI chatbot market is expanding rapidly as the tech sector leverages Transformer Neural Network Architecture, which is particularly useful for handling natural language processing (NLP) tasks. This approach, which originated from Google’s research, was used to build models like ChatGPT, Bard, and other prominent language models, and continues to drive modern advancements in processing textual data.
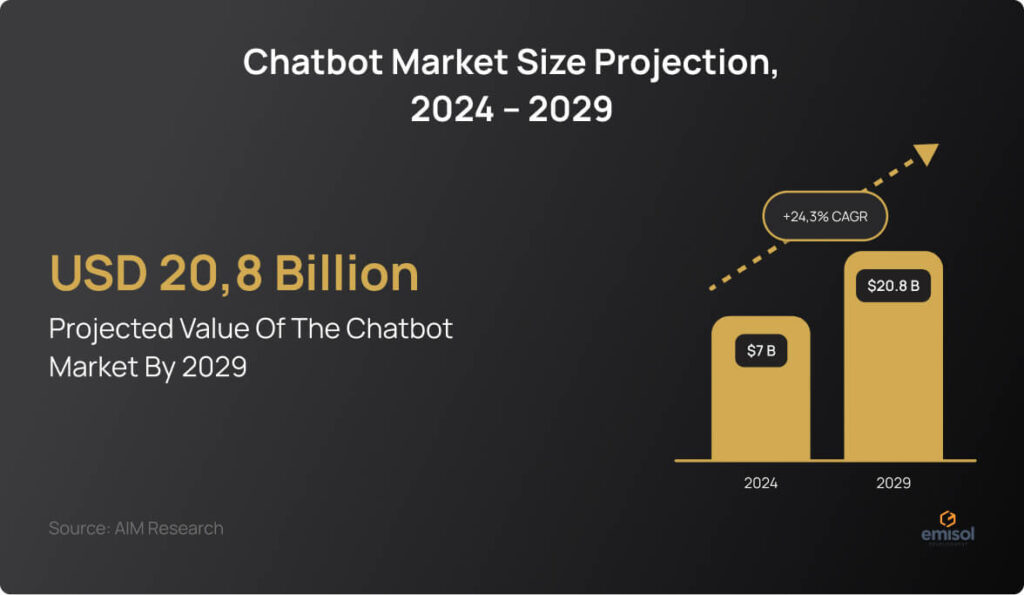
According to AIM Research, the chatbot market is valued at USD 7 billion in 2024 and is projected to soar to USD 20.8 billion by 2029, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.3%. This surge is driven mainly by substantial investments from big tech companies in large language models (LLMs), which have paved the way for the proliferation of AI chatbots.
Challenges and Opportunities in AI Chatbot Development
However, the cost of developing custom large language models is prohibitively high for many companies. For instance, training OpenAI’s GPT-4 reportedly required around USD 78 million in compute resources, while Google’s Gemini Ultra incurred a staggering cost of USD 191 million. Moreover, predictions suggest that training new LLMs could reach USD 100 billion in the next three to five years, as these models become even more sophisticated and resource-intensive.
Fortunately, the release of these models to the public has opened doors for many companies to integrate generative AI into their operations without having to develop complex LLMs from scratch (though using these models is not free for businesses). As of 2024, businesses worldwide are seizing the opportunity to incorporate language models into their processes. The most common applications of AI language models today include virtual assistants, help desks, personalized recommendation systems, messaging platforms, and other environments where handling complex user queries is essential.
At Emisol, we have a team of experts skilled in developing custom AI chatbots tailored to specific business needs and niches. Recently, we built a messenger app that integrates an AI chatbot to filter user-generated content that doesn’t comply with Sharia laws. The potential applications of AI chatbots are vast, and in this article, we will explore the different aspects of AI chatbot development in 2024 and how organizations can incorporate this technology into their workflows.
What is an AI Chatbot?
Early chatbot development relied on pattern-matching techniques, matching input phrases to predefined templates based on keywords or structures, as seen in early chatbots like Eliza and ALICE. While effective for simple, domain-specific conversations, this approach was limited by repetitive responses and lack of memory, making it less suitable for complex interactions and large-scale applications.
In contrast to the earlier chatbots, chatbots such as ChatGPT make use of generative AI, large language models (LLMs), natural language understanding (NLU), and natural language processing (NLP) to handle user queries. Thanks to conversational AI, these chatbots are pieces of software that can understand human language outside of a pre-defined context. AI chatbots can write code, generate article ideas, compose emails, create videos and images, and much more at a user’s command. Modern AI chatbots are trained with immense datasets and retain information from conversations for future learning.
AI chatbots can also learn from each interaction and adjust their actions to provide better responses. While simple chatbots work best with straightforward, frequently asked prompts, chatbots that leverage technology like generative AI can handle more sophisticated requests. This includes anticipating user needs and supporting users using natural human language. AI-powered chatbots can be applied to a wide range of use cases, such as customer service, analyzing a customer’s complaints, making predictions about what a site visitor is looking for on your website, or writing a personalized email to a prospect.
How Do AI Chatbots Work? Understanding the Technology Behind Conversational Agents
As chatbot technology advanced, algorithms enabled more sophisticated rule-based programming and natural language processing, allowing bots to engage in conversational interactions. This led to a new generation of chatbots—context-aware and powered by machine learning—which improve their ability to process and predict user queries through continuous exposure to language data.
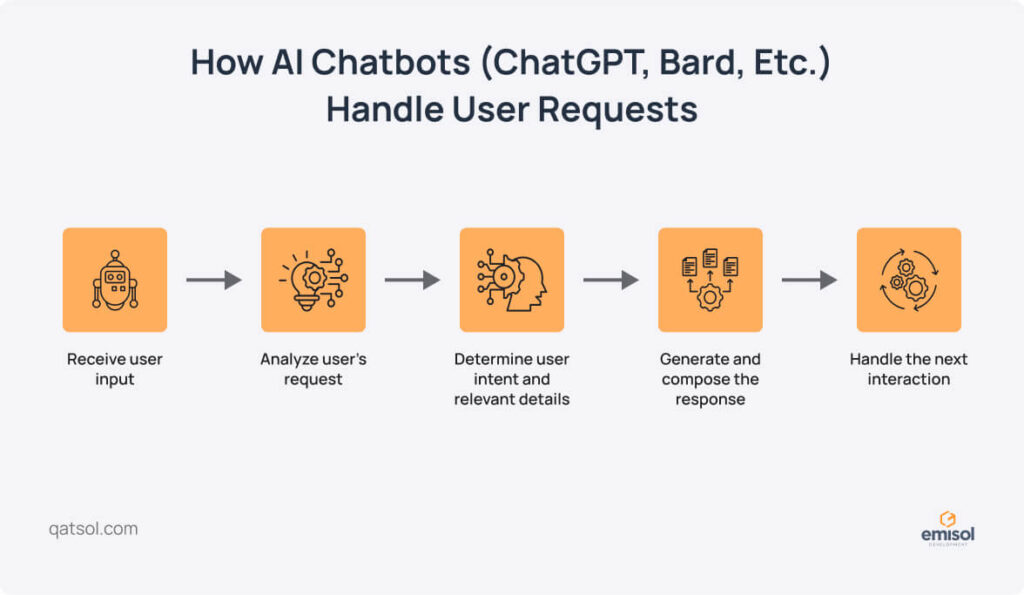
A typical chatbot interaction flow looks like this:
- A user initiates a conversation by typing or speaking through the chatbot interface.
- The chatbot analyzes the input using NLP to understand the user’s intent.
- It searches its database for the most relevant response.
- The chatbot replies through the same interface.
- The conversation continues as the user responds, repeating the process until it concludes.
At its core, an AI chatbot processes input and generates a relevant response. For instance, when a user asks a question, the AI interprets their intent—considering tone and sentiment—and delivers the most appropriate answer.
AI chatbots need large amounts of conversational data for effective training. During this phase, developers teach the chatbot to understand the context of human language. This contextual understanding enables AI assistants to handle complex queries naturally and conversationally.
Types of AI Chatbots: From Rule-Based to Advanced Conversational AI
AI chatbots have come a long way from their basic origins. Today, they’re essential tools in many industries, helping businesses deliver fast and efficient service. But not all chatbots are created equal—each type has its own strengths, tailored to different needs. To make the most of them, it’s important to understand the variety of AI chatbots out there and what they bring to the table. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of AI chatbots, explained in a more approachable way.
Rule-Based Chatbots (Decision Tree Chatbots)
Ever found yourself clicking through a series of options, like a flowchart guiding you step by step?
That’s the essence of a rule-based chatbot. These bots are predictable, sticking to a script with every response pre-programmed in advance. You ask a question, and they respond with set options—they know their lines and never go off-script.
If you’re looking to get something done quickly—like booking an appointment or getting an answer to a common query—this type of chatbot is perfect. It’s not here to chat or dazzle, but it’s efficient, task-focused, and, well, reliable.
No surprises, just straightforward service.
Retrieval-Based Chatbots (NLP Chatbots)
Let’s be honest, it’s annoying when you have to word your questions a certain way to get the right response.
Retrieval-based chatbots aim to fix that by understanding natural language, much like a real conversation. They don’t need you to press buttons or carefully pick keywords—they get what you’re asking (well, most of the time).
But here’s the catch—they still rely on pre-written responses. They’re better at figuring out the intent behind your question, but their answers are still pulled from a set database. So, while you’ll notice the difference compared to more rigid bots, they’re not quite at the “let’s have a deep conversation” level yet.
Generative Chatbots (Conversational AI)
These chatbots don’t just recycle old responses—they generate new ones on the fly, which makes the conversation feel far more human. They don’t just hear what you say; they think through it.
Want a chatbot that can handle nuance and even sound like it’s considering your words? Generative chatbots are your pick.
And here’s what separates them from more basic versions—they remember. They keep track of the conversation, so it feels more like an ongoing dialogue than just a series of disconnected replies. Whether you’re asking for a product recommendation or troubleshooting an issue, these bots respond based on everything you’ve said up to that point.
Most generative AI chatbots you’ve encountered or used are built on architectures powered by models like OpenAI’s GPT or Google’s Gemini.
Contextual AI Chatbots (Advanced Conversational AI)
Ever wished a chatbot could actually remember you? That’s what contextual AI chatbots are all about. They don’t just respond to one-off questions; they retain information from past conversations. Imagine talking to a customer service bot today and it remembering the details when you come back next week.
Not only that, these bots can pull real-time data into their responses. Ask about your package, and they’ll check the live tracking status before answering you.
The more you interact with them, the more accurate and helpful they get. It’s like they learn your preferences over time, adapting to your needs.
Hybrid Chatbots (Combining AI and Rule-Based)
What if you could mix the best parts of both rule-based and AI-driven bots? Hybrid chatbots do exactly that.
They switch between straightforward, rule-based answers when things are simple and AI-powered responses when questions get tricky. It’s flexibility at its finest.
For example, if you ask a simple question, they will give you a quick, rule-based reply. But if you ask something that needs more context, they dig into the AI side of things, providing a deeper, more profound response.
And if the AI gets stuck? No worries—they can fall back on the rules. You never hit a dead end with these bots.
Voice-Activated AI Chatbots
Voice-activated chatbots let you skip the keyboard and just talk. Whether you’re asking for directions while driving or checking your schedule during breakfast, voice chatbots make it feel like you’re talking to an actual assistant—without the typing hassle.
These bots respond in real-time, making the conversation feel fluid and immediate. Need quick info or want to multitask without touching your device? This is where voice-activated AI shines. It’s hands-free and intuitive, just like a real conversation.
Each of these chatbot types brings something different to the table. Whether you need a bot that sticks to the script or one that adapts to your every word, there’s an AI out there designed to make your interactions smoother. Which one sounds like it’d make your life easier?
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Build a Custom AI Chatbot for Your Business
Let’s dive deep into how you can create an AI chatbot from the ground up.
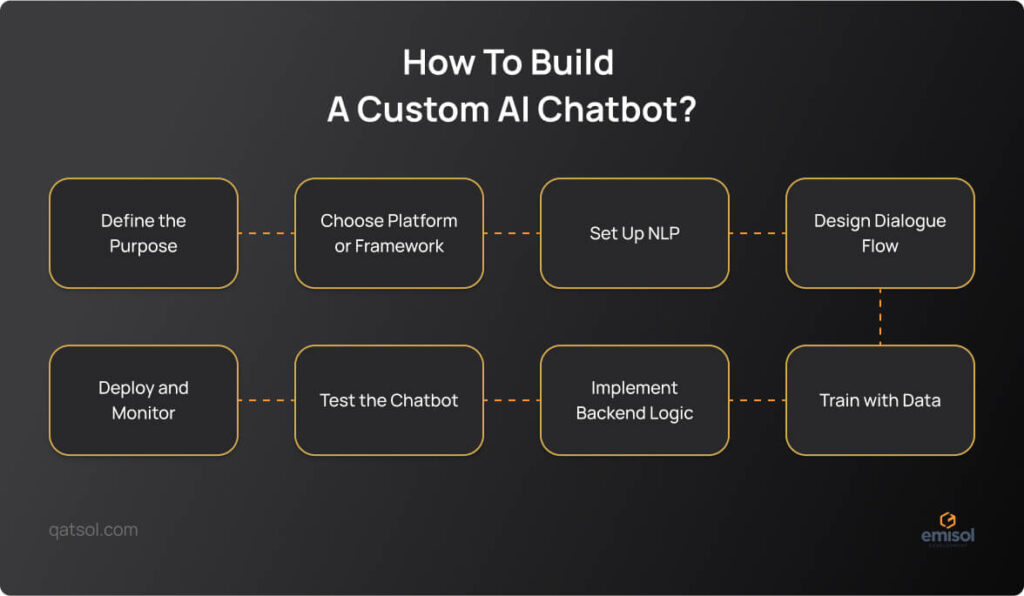
Step 1: Define the Purpose of Your AI Chatbot
Before diving into the code, you need a clear understanding of what your chatbot will do.
What problem will it solve?
Will it answer customer queries, automate routine tasks, or provide recommendations? Defining the scope upfront helps narrow down the technology and features you’ll need to implement.
For instance, if you want your chatbot to handle customer support, you’ll need to think about the types of questions it will receive, the data it will access (e.g., order status, information from CRM, or FAQs), and how conversational it needs to be.
A bot that schedules meetings might be much simpler than one designed to manage entire customer interactions.
Step 2: Choose the Right Platform or Framework
When it comes to building a chatbot, you’ve got choices. You can either build it from scratch using programming languages like Python or Node.js, or you can leverage chatbot development platforms that come with built-in tools.
If you’re starting from scratch, libraries like TensorFlow or PyTorch for machine learning, and NLTK or spaCy for natural language processing, are excellent starting points. These tools allow you to train your chatbot to understand human language.
Alternatively, platforms like Rasa or Dialogflow offer a more structured approach. They give you access to pre-built AI models and simplify the process of integrating NLP and machine learning.
Step 3: Set Up Natural Language Processing
For your chatbot to understand user inputs, it needs to be equipped with Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP enables the chatbot to break down user queries, analyze their meaning, and respond appropriately.
Start by setting up an NLP pipeline. This pipeline processes the text, extracting important pieces of information such as keywords, intent, entities (like names or dates), and sentiment. Tools like spaCy, NLTK, or Transformers (from Hugging Face) can be used for building custom NLP models.
You’ll need to:
- Tokenize the text: Break down the user’s message into individual words or tokens.
- Remove stop words: Filter out common but irrelevant words like “the”, “is”, “in.”
- Understand intent: Use machine learning to detect what the user is trying to achieve.
- Extract entities: Identify specific data like dates, locations, or product names.
For example, if a user asks, “When will my order be delivered?” your chatbot should recognize that “order” is an entity, and “delivered” is the intent. Based on this, it will search for delivery status information.

Step 4: Design the Chatbot’s Dialogue Flow
This is where the art of conversation design comes in. Your chatbot needs to guide users through a conversation in a natural and intuitive way, so mapping out potential dialogues is paramount.
Start by creating user stories or flowcharts for various conversation paths. Think about the questions users will ask and how your bot should respond. Include both happy path (ideal) and edge case (unexpected) scenarios.
For example:
- User: “I’d like to check my order status.”
- Your bot: “Please provide your order ID.”
- User: “219014.”
- Your bot: “Your order is on its way and will be delivered by 5 PM tomorrow. Is there something else I can help you with?”
Make sure your chatbot can handle various ways users might phrase the same question. Flexibility is critical to a good user experience.
Step 5: Train the Chatbot with Data
A chatbot is only as good as the data it’s trained on. Consider this quote from Dave Friend, the co-founder and CEO of Wasabi:
For example:
- User: “I’d like to check my order status.”
- Your bot: “Please provide your order ID.”
- User: “219014.”
- Your bot: “Your order is on its way and will be delivered by 5 PM tomorrow. Is there something else I can help you with?”
Make sure your chatbot can handle various ways users might phrase the same question. Flexibility is critical to a good user experience.
“At the heart of AI is data. The more complete the data on which an AI is trained, the more valuable will be the output.”
This is where you need to feed it real-world conversational data. The more examples it sees, the better it will become at predicting user intent and generating appropriate responses.
Start by collecting training data. This could be historical customer service logs, FAQs, emails, CRM entries, or any other interaction data you have. For NLP models, the data needs to be labeled with intents and entities so the machine learning model can learn from it.
For example, you could provide data like:
- “Check order status” -> Intent: CheckOrder
- “When will my order arrive?” -> Intent: CheckOrder
- “Cancel my subscription” -> Intent: CancelSubscription
Once you have enough training data, you’ll need to feed it into a machine learning model. You can use algorithms like Support Vector Machines (SVMs), Decision Trees, or more advanced deep learning models like Transformers to train the chatbot to recognize patterns in user queries.
Step 6: Implement the Backend Logic
Your bot will likely need to pull data from a database, CRM, or API to provide accurate responses. For instance, if your chatbot handles customer service inquiries, it should be able to access order status, product availability, or account information in real-time.
For this, you’ll need to write backend code that can fetch, process, and return data as required by the chatbot. Common technologies include:
- For this, you’ll need to write backend code that can fetch, process, and return data as required by the chatbot. Common technologies include:
- Databases: For storing and retrieving user data, orders, or interaction logs.
- Webhooks: For real-time notifications when certain conditions are met (e.g., “Your package has shipped!”).
Step 7: Test, Test, and Test Again
Once your chatbot is functional, it’s time to test it rigorously. Testing is crucial because it ensures that your bot can handle a wide variety of user inputs and edge cases.
Start with unit tests to ensure each component of the bot—NLP, machine learning models, and backend—works as expected. Then move to user testing where real people interact with your chatbot. This will help you identify any gaps in its understanding or logic flow.
Simulate different conversation types, unexpected questions, or interruptions to see how the chatbot handles them. Make sure your chatbot can gracefully handle mistakes—whether by providing clarification or redirecting to a human agent when needed.
Step 8: Deploy and Monitor the Chatbot
Now it’s time to launch! Whether you’re deploying on your website, mobile app, or messaging platforms like Slack or Facebook Messenger, the integration process should be seamless.
After deployment, it’s critical to monitor your chatbot’s performance. Use analytics tools to track interactions, success rates, and user feedback. Look for metrics like:
- Accuracy: How well the chatbot understands and answers user queries.
- Engagement: How often users interact with the bot and complete actions.
- Drop-off points: Where in the conversation flow users tend to leave.
How AI Chatbots Are Transforming Industries
Hospitality
In the hospitality and entertainment industry, AI chatbots can significantly enhance guest experiences and streamline operations. For instance, a hotel can deploy a chatbot on its website and mobile app to assist guests with various needs. The chatbot can handle pre-check-in processes, such as room preferences and booking additional services, provide 24/7 concierge support by offering recommendations and booking local dining or entertainment options, and manage post-stay follow-ups to gather feedback and offer discounts on future stays.
While chatbots offer considerable benefits, including personalized guest interactions and operational efficiency, they come with risks.
Learn more about the recent case of Air Canada’s chatbot giving incorrect information to a traveler (a discount that wasn’t available), which led to legal proceedings.
Chatbots may occasionally provide incorrect or misleading information, leading to potential guest dissatisfaction or legal complications. They also require strict data privacy measures to protect sensitive guest information and may result in reduced personal interactions if overused. Regular maintenance and updates are crucial to ensure the chatbot remains accurate and effective in addressing guest needs.
Finance
In the finance sector, AI chatbots can transform customer interactions by handling a range of tasks that traditionally required human agents. For example, a financial institution might implement a chatbot to assist customers with checking account balances, reviewing transaction histories, and setting up recurring payments. The chatbot can also offer personalized financial advice, such as budgeting tips or investment recommendations, based on the user’s financial behavior and goals.
Additionally, the chatbot can facilitate loan applications by guiding users through the required documentation and eligibility criteria, and provide real-time alerts for suspicious account activity or unusual transactions. This reduces the need for human intervention and enhances overall customer satisfaction by providing instant, reliable support.
Education
In education, AI chatbots play a crucial role in enhancing student engagement and support. For instance, an educational institution might deploy a chatbot to assist prospective students with inquiries about admission requirements, scholarship opportunities, and program details. Once enrolled, students can interact with the chatbot to get information on class schedules, deadlines for assignments, and exam preparation tips.
The chatbot can also provide personalized learning support by offering additional resources or exercises tailored to the student’s current coursework and performance. Moreover, it can automate administrative tasks such as scheduling appointments with academic advisors or managing student feedback, streamlining processes and improving the overall educational experience.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, AI chatbots can significantly boost operational efficiency and support. For example, a manufacturing company might use a chatbot to manage maintenance requests for machinery, providing real-time updates on the status of repairs and scheduling preventive maintenance based on usage data. The chatbot can also assist in inventory management by tracking stock levels and alerting procurement teams when supplies are low.
Additionally, it can streamline internal communications by answering employee questions about safety protocols, operational procedures, and HR policies. This reduces the need for manual intervention and improves overall workflow efficiency, contributing to a more streamlined and effective manufacturing process.
Retail
In retail, AI chatbots enhance the customer experience by providing personalized and efficient service. For example, an online retailer might integrate a chatbot to assist customers with finding products based on their search history and preferences. The chatbot can offer tailored product recommendations, help with product comparisons, and provide detailed information about promotions or sales.
During the checkout process, the chatbot can assist with order modifications, apply discount codes, and address any payment issues. Post-purchase, the chatbot can help with tracking orders, managing returns or exchanges, and collecting feedback to improve future shopping experiences. This ensures a smooth and engaging shopping journey for customers.
How Emisol Can Help
From the basic rule-based systems of the past to today’s advanced AI chatbots, the journey showcases the incredible advancements in artificial intelligence. Building a custom AI chatbot involves a detailed process, from defining its purpose to continuous optimization. AI chatbots offer numerous benefits, including enhanced customer service, streamlined operations, and personalized user experiences.
Ready to harness the power of AI chatbots for your business? Connect with us at Emisol to explore how our tailored solutions can elevate your digital interactions and drive innovation.




